Description
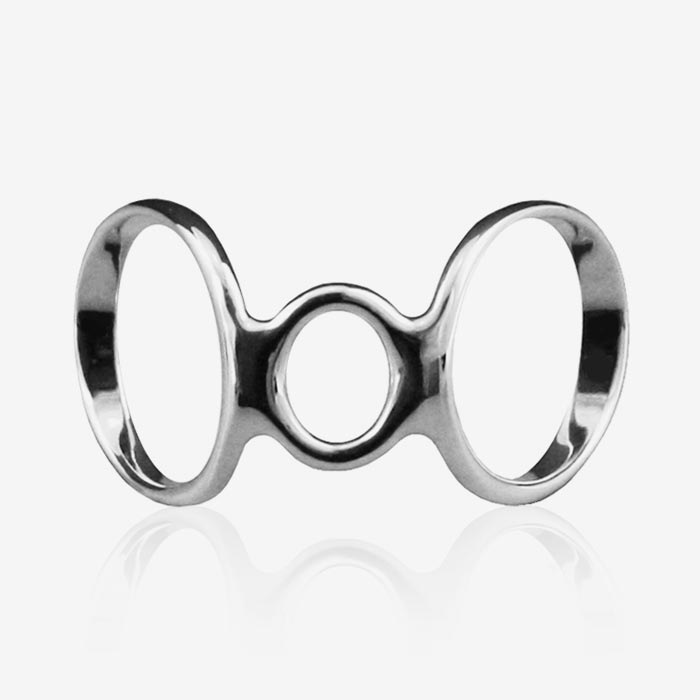
SilverRing™ Boutonniere Splint for Hyperextension
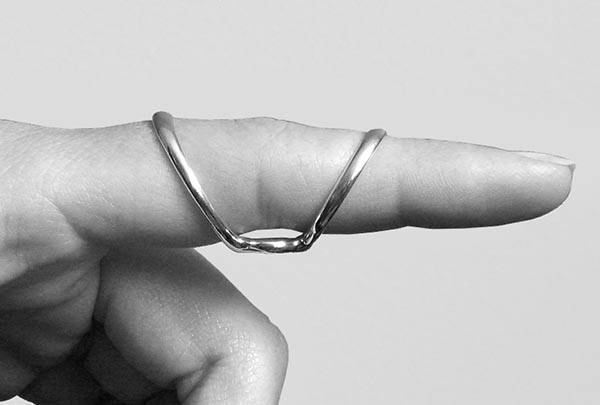
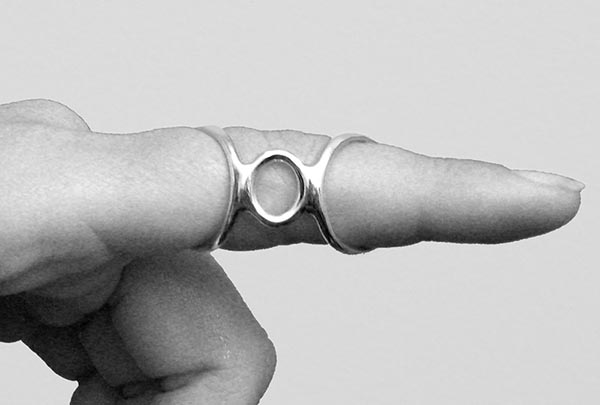
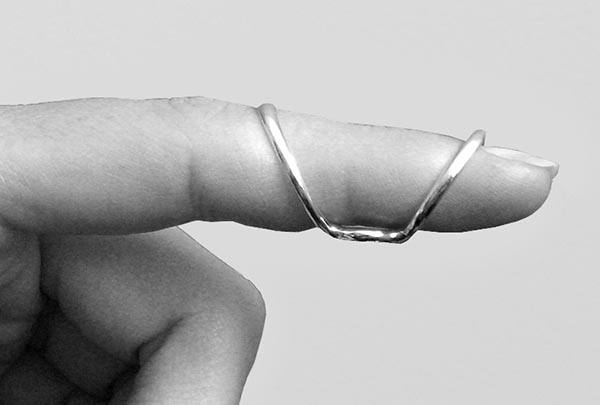
Use the SilverRing™ Boutonniere Splint for severe hyperextension (greater than 20 degrees) or when subluxation of the joint is occurring. This splint is worn with the oval spacer under the joint to block hyperextension while allowing full flexion. It positions the two rings farther from the joint for better leverage at a more comfortable angle.
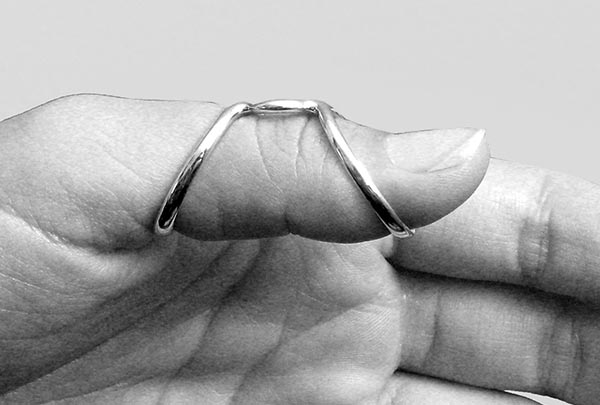
SilverRing™ Boutonniere Splint for Lateral Instability
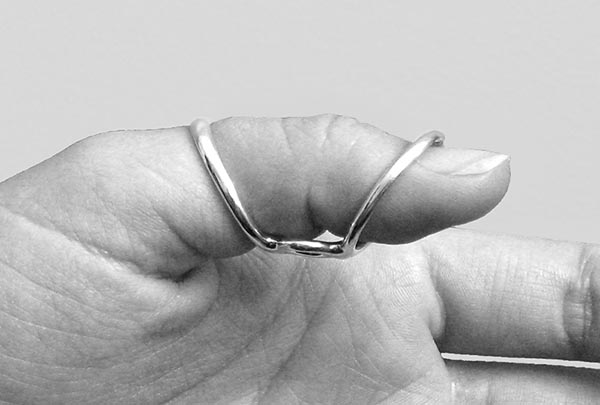
Use the SilverRing™ Boutonniere Splint, worn with the spacer on the side of the joint, for lateral instability with limited range of motion. This splint provides the greatest leverage for correcting joint deviation when flexion of the joint is limited to less than 45 degrees, but not for a finger which has full active flexion since the splint will rotate. The SilverRing™ Boutonniere Splint can be used on the DIP joint, the PIP joint of a short finger or the IP joint of the thumb.
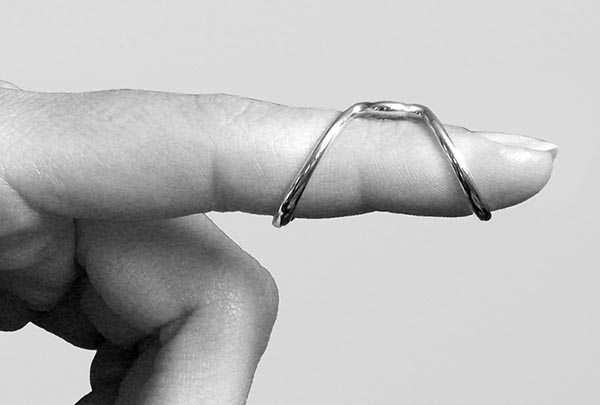
SilverRing™ Boutonniere Splint for Flexion
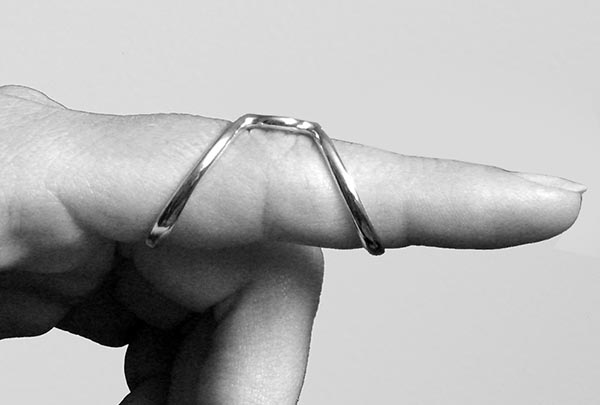
The SilverRing™ Boutonniere Splint can be used for both reducible flexion and mild to moderate non-reducible flexion. Use this splint to correct a reducible boutonniere or mallet finger deformity. The wearer can adjust this splint to hold the finger in position and provide varying degrees of extension mobilization. When using the SilverRing™ Boutonniere Splint to correct a mild to moderate non-reducible boutonniere or mallet finger contracture (less than 25 degrees), the individual ring sizes must be larger than normal since the splint must accommodate the contracture.